DevOps is a combination of software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops), Which shorten the systems development life cycle and provide continuous delivery with high software quality. It is complementary with Agile software development; several aspects of DevOps have come from Agile methodology.
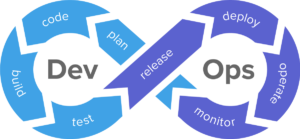
As DevOps is intended to be a cross-functional mode of working, those who practice the methodology use different sets of tools—referred to as “toolchains”—rather than a single one.These toolchains are expected to fit into one or more of the following categories, reflective of key aspects of the development and delivery process:
- Coding – code development and review, source code management tools, code merging.
- Building – continuous integration tools, build status.
- Testing – continuous testing tools that provide quick and timely feedback on business risks.
- Packaging – artifact repository, application pre-deployment staging.
- Releasing – change management, release approvals, release automation.
- Configuring – infrastructure configuration and management, infrastructure as code
- Monitoring – applications performance monitoring, end-user experience.
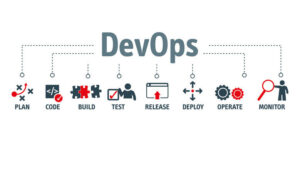
Some categories are more essential in a DevOps toolchain than others; especially continuous integration (e.g. Jenkins, Gitlab, Bitbucket pipelines) and infrastructure as code (e.g., Terraform, Ansible, Puppet).
Forsgren et al. found that IT performance is strongly correlated with DevOps practices like source code management and continuous delivery.